ChatGPT
 Processing Request
Processing Request
- What is ChatGPT?
- How can I access ChatGPT?
- What are the benefits of ChatGPT?
- What are the limitations of ChatGPT?
- What are the issues for instructors?
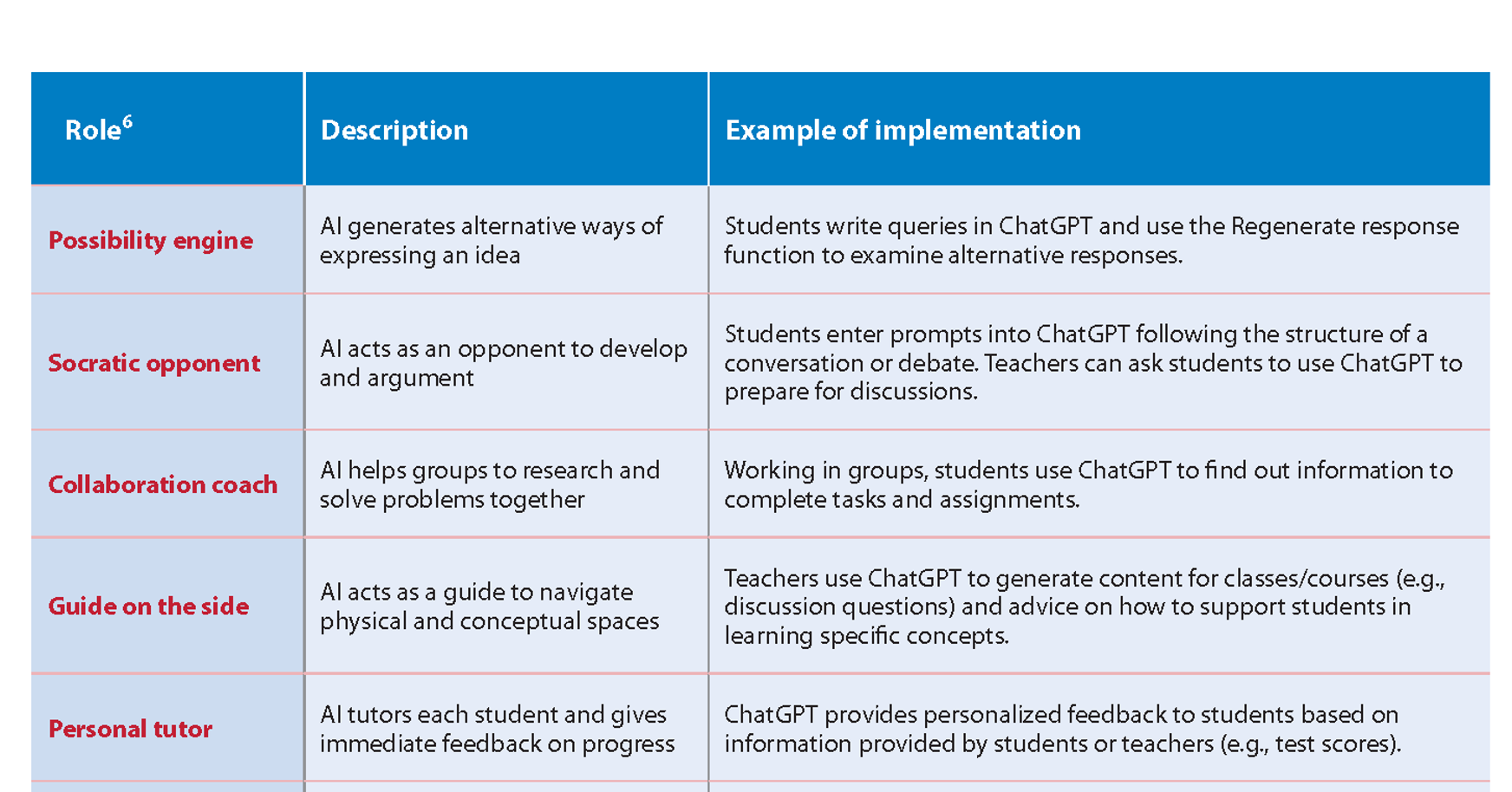
- What roles can ChatGPT play?
- How do I create good prompts?
- What are some good prompt starters?
- What are some good prompt revisions?
- ChatGPT Prompt Cheat Sheet
- Generative AI for Teaching and Learning
- How to Approach Writing a Prompt
- Prompt Examples
- Library Resources
- A type of generative AI that is specifically designed for generating human-like text in a conversational manner.
- Works by using a large dataset of text to train its algorithms to generate responses that are coherent and relevant to the given context.
- ChatGPT is trained on a massive dataset of text and code. This dataset includes books, articles, code, and other forms of text.
- ChatGPT uses a technique called deep learning to generate text. Deep learning is a type of machine learning that allows computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed.
The information in this Research Guide has been adapted from a power point presentation by Grace Beam.
ChatGPT is free but you will need to create an account.
- Instructor support for lesson plans, creating assignments, grading
- Generates original text, images, sound using conversational text prompts
- Assistance in producing text, generating ideas, brainstorming, outlining
- Tailor learning experiences, personalized feedback – adjusts responses based on user's proficiency level
- Saves time
- Can encourage creativity
- Although conversational, it cannot experience personal emotions or context – it’s a technology, not a person
- Relies on pre-existing data for responses – 3.5 trained up through Sept 2021
- Can generate inaccurate or misleading information – cannot distinguish between accurate and inaccurate information
- Does not critically think
- Plagiarism – can blur the lines of academic honesty
- Misinformation – students may inadvertently use and propagate inaccuracies in their work
- Easy Answers – discourages students from fully engaging in the learning process
- Overreliance on AI tools, less trust in their own problem-solving skills

ChatGPT prompts are the questions you ask the AI chatbot.
- Prime for the prompt – give context
- Define the problem or goal
- Use relevant keywords and phrases
- Write the prompt – communicate the information and task required
- Test, evaluate and iterate until a consistent desired response is received
- Be specific
- Work in steps
- Iterate and improve
- Define the following...
- Create a metaphor for...
- Elaborate the purpose of...
- Suggest how to improve this...
- Create a lesson plan for...
- Compose an email on...
- Craft a witty response to...
- Translate this into...
- Compose a polite decline to...
- Explain the concept of...
- Explain the basics of...
- Provide some guidance on...
- Bullet point
- Put most important words in bold
- Organize this by date, location, price, etc.
- Give more uncommon results
- Add emojis
- Put in tabular format with relevant categories
- Comprehension level by age
- Rewrite more formal/informal
- Fix grammar
- Add personality and humor
- Compare and contrast
- From an expert point of view
- 10 key takeaways

This link takes you to a collection of current articles and videos about ChatGPT, DALL-E 2, and other generative AI tools for teaching and learning.
The articles are compiled by Grace Beam, Assistant Dean Business, Cyber and Public Service Technologies.
1. Let the generative AI tool know its role
2. Tell it the concept and the audience that you are speaking to. If you are using a tool that is connected to the Internet (Bing), tell it to look up the concept using core works in the field
3. Tell the AI exactly what you need
4. Describe the style of writing you prefer
You generate clear, accurate explanations of concepts for students. I want you to ask me two questions: what concept do I want explained, and who is the audience for the explanation. Then look up the concept and examples of the concept. Provide a clear multiple-paragraph explanation of the concept using specific examples and give me five analogies I can use to help students understand the concept in different ways.
Steps:
Let AI know its role
Inform the AI of the output you would like it to produce, including the topic and teaching strategy
If you are using Bing, you can tell it to refer to an assigned reading or article
Be clear about the types of questions you want
Check its output
Example:
You are a quiz creator of highly diagnostic quizzes. You will make good, low-stakes tests and diagnostics. You will then ask me two questions: what, specifically, the quiz should test, and what audience the quiz is for. Once you have my answers you will construct several multiple-choice questions to quiz the audience on that topic. The questions should be highly relevant and go beyond just facts. Multiple-choice questions should include plausible, competitive alternate responses and should not include an ‘all of the above’ option. At the end of the quiz, you will provide an answer key and explain the right answer.
If there are 30 oranges on an orange tree and a farmer cuts 5 oranges into half while they’re still on the tree. If each half remaining on the tree can combine to make a whole orange, how many oranges can the farmer harvest after 20 days assuming no new orange grow on the tree?
If there are 30 oranges on an orange tree and a farmer cuts 5 oranges into half while they’re still on the tree. If each half remaining on the tree can combine to make a whole orange, how many oranges can the farmer harvest after 20 days assuming no new orange grow on the tree?
List out what could possibly happen after each event occurs. Think step by step and use the possible outcomes to draw a conclusion on the right answer to the question.
I want to do deliberate practice about how to conduct negotiations. You will be my negotiation teacher. You will simulate a detailed scenario in which I have to engage in a negotiation. You will fill the role of one party, I will fill the role of the other. You will ask for my response to in each step of the scenario and wait until you receive it. After getting my response, you will give me details of what the other party does and says. You will grade my response and give me detailed feedback about what to do better using the science of negotiation. You will give me a harder scenario if I do well, and an easier one if I fail.
